QFP (Quad Flat Package)
Update Time: Dec 06, 2023 Readership: 902
Contents
Quad Flat Pack (QFP) is an integrated circuit (IC) packaging technology that plays an important role in the field of IC packaging. QFP is a surface mount package that is widely used in the IC industry, especially in applications requiring relatively large pin counts, such as consumer electronics, communication equipment, and industrial control systems.
Although QFP is a relatively mature packaging technology, it is still innovating in order to cater to the increasing needs of modern electronic devices for size, performance and cost. These innovations drive the continuous evolution of QFP technology and bring more possibilities to the entire integrated circuit industry to meet changing market demands. Today, we’re going to talk about it in depth and go a little further into it.
What is a Quad Flat Package
A Quad Flat Package (QFP) is a type of surface-mounted integrated circuit (IC) package that features distinctive "gull wing" leads extending from each of its four sides. This packaging design enhances the ease of soldering and facilitates surface mounting on printed circuit boards (PCBs). Unlike traditional through-hole mounting, QFP is not designed for socketing, making direct soldering onto the PCB the standard method of attachment.
QFPs are characterized by a variety of specifications, including the number of pins and the pitch between these pins. The pins are the electrical connections that link the IC to the external circuitry on the PCB. QFPs come in a range of pin counts, commonly ranging from 32 to 304 pins, catering to a wide spectrum of applications with varying degrees of complexity. The pitch, or the distance between adjacent pins, typically falls within the range of 0.4 to 1.0 mm, allowing for flexibility in design and accommodating different requirements for miniaturization.
The "gull wing" leads, shaped like the wings of a seagull, provide mechanical support and ensure a secure connection during the soldering process. This design allows for a compact footprint on the PCB, making QFPs suitable for applications where space efficiency is crucial.
QFP Package Sizes
Example of QFP Package Sizes
QFP (Quad Flat Package) comes in a variety of sizes to meet the diverse needs of integrated circuits (ICs) in different applications. The thickness, pin count, lead pitch, and overall dimensions play crucial roles in determining the suitability of a QFP for a specific electronic device.
-
Regular QFP Thickness
Traditional or regular QFPs typically exhibit thicknesses ranging from 2.0 to 3.8 mm. This thickness provides a balance between structural integrity and the need for a compact profile. The larger the package size (measured in pins), the thicker the QFP tends to be, as it needs to accommodate a greater number of leads and provide sufficient space for the integrated circuit.
-
Thin Quad Flat Package (TQFP)
Thickness Range: TQFP packages are designed with a reduced thickness compared to regular QFPs. They offer a slimmer profile, which is advantageous in applications where space constraints are critical.
Example Sizes:
A TQFP package with 32 pins might have a lead pitch of 0.8 mm, with overall dimensions of 5 mm by 5 mm and a thickness of 1 mm.
For a larger TQFP with 256 pins, the package might measure 28 mm by 28 mm, have a thickness of 1.4 mm, and feature a finer lead pitch of 0.4 mm. This finer pitch allows for a higher pin density, making it suitable for more complex ICs.
-
Lead Pitch and Pin Count
The lead pitch refers to the distance between the centers of adjacent pins. Smaller lead pitches are associated with higher pin densities, allowing for more connections in a given area. As mentioned, regular QFPs and TQFPs can have lead pitches ranging from 0.4 to 1.0 mm, depending on the specific requirements of the IC and the application.
QFP package sizes vary to accommodate a spectrum of applications, from compact and thin TQFPs suitable for space-constrained devices to regular QFPs with larger dimensions for more complex integrated circuits. Engineers and designers carefully evaluate these dimensions to choose the most suitable QFP for their specific electronic system requirements.
QFN vs. QFP Packaging: What are the Differences

Conclusion Table
In summary, the key differences between QFP (Quad Flat Package) and QFN (Quad Flat No-Lead) packaging lie in their lead configuration, size, number of pins, and lead pitch:
-
Lead Configuration
The key difference in lead configuration between Quad Flat Package (QFP) and Quad Flat No-Lead (QFN) packaging lies in how they connect to a printed circuit board (PCB). QFP has leads or pins extending from the sides and bottom, allowing for through-hole or surface mount connections. In contrast, QFN lacks leads on the sides, and its connections are made through pads on the bottom surface, using surface mount technology.
-
Size
Size is a notable contrast between Quad Flat Package (QFP) and Quad Flat No-Lead (QFN) packaging. QFP is typically larger because of the leads extending from its sides and bottom. These protruding leads allow for through-hole or surface mount connections but contribute to a larger physical footprint on the printed circuit board (PCB). On the other hand, QFN is generally smaller and more compact as it lacks protruding leads. The absence of these leads on the sides makes QFN well-suited for applications where space efficiency is crucial.
-
Number of Pins
The number of pins is a significant distinction between Quad Flat Package (QFP) and Quad Flat No-Lead (QFN) packaging. QFP can accommodate a higher number of pins, ranging from 32 to well over 100. This design makes QFP suitable for components demanding numerous connections, such as integrated circuits (ICs) in complex electronic systems. In contrast, QFN typically has fewer pins, usually less than 32. The reduced pin count aligns with applications where a lower number of connections is sufficient. QFN's design is well-suited for components with less intricate connectivity requirements, contributing to its use in various electronic devices where a compact form factor is essential.
-
Lead Pitch
Lead pitch, or the distance between adjacent leads, distinguishes Quad Flat Package (QFP) and Quad Flat No-Lead (QFN) packaging. QFP has a smaller lead pitch, enabling a higher pin density on the package and the PCB. In contrast, QFN generally has a larger lead pitch, resulting in a less dense pin configuration. This difference influences the overall size, complexity, and manufacturing considerations, guiding the choice between QFP and QFN based on specific application requirements.
In practical terms, QFP is often chosen for components demanding a high pin count and a larger physical footprint on the PCB, such as microcontrollers in industrial applications. On the other hand, QFN is favored for components with fewer connections and a need for space efficiency, common in applications like consumer electronics and miniaturized devices. The choice between QFP and QFN depends on the specific requirements of the electronic system and the desired balance between size, pin count, and assembly technology.
TQFP vs LQFP: What is the Difference
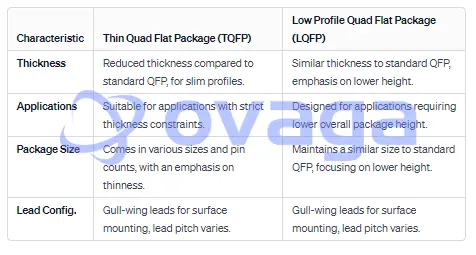
Conclusion Table
Thin Quad Flat Package (TQFP) and Low Profile Quad Flat Package (LQFP) are variations of the Quad Flat Package (QFP), each with specific design characteristics.
-
Thickness
As the name suggests, TQFP is characterized by a reduced thickness compared to standard QFP. This design is aimed at providing a thinner profile, making it suitable for applications with stringent space constraints.
LQFP, on the other hand, emphasizes a lower overall height while maintaining a similar thickness to standard QFP. The emphasis is on reducing the package's height rather than making it significantly thinner.
-
Applications
TQFP is often chosen for applications where minimizing the overall thickness of the device is crucial. This makes it suitable for slim-profile electronic devices and systems with limited vertical space.
LQFP is designed to address applications where a lower overall package height is a priority, but not necessarily a significant reduction in thickness. It is well-suited for devices where vertical space is constrained, and a flatter profile is desired.
-
Package Size
TQFP, like standard QFP, comes in various sizes and pin counts, but the emphasis is on providing a thinner form factor.
LQFP maintains a similar size to standard QFP but with a lower overall profile.
-
Lead Configuration and Pitch
Both TQFP and LQFP typically have gull-wing leads that facilitate surface mounting on a PCB. The lead pitch (distance between adjacent leads) can vary based on the specific design and requirements.
While TQFP focuses on reducing overall thickness for applications with strict space constraints, LQFP aims to maintain a similar thickness to standard QFP while emphasizing a lower overall package height.
Different Types of QFP
Quad Flat Package (QFP) comes in various types and variations to meet specific design requirements.
-
Standard QFP
This is the traditional Quad Flat Package with pins extending from all four sides.
-
Thin QFP (TQFP)
TQFP is designed with a reduced thickness compared to standard QFP. It is suitable for applications where minimizing the overall thickness of the device is crucial.
-
Very Thin QFP (VQFP)
VQFP takes the concept of reduced thickness further than TQFP. It is an even thinner variant designed for applications requiring an extremely slim profile.
-
Low-Profile QFP (LQFP)
LQFP emphasizes a lower overall height while maintaining a similar thickness to standard QFP. It is suitable for applications where reducing the package's height is a priority, but not necessarily making it significantly thinner.
-
Plastic Quad Flat Package (PQFP)
PQFP is a type of QFP where the package material is plastic. This is in contrast to ceramic QFP, which uses ceramic as the package material.
-
Ceramic Quad Flat Package (CQFP)
CQFP utilizes ceramic as the package material. Ceramic packages offer better thermal performance compared to plastic, making them suitable for applications where heat dissipation is a critical factor.
-
Enhanced Quad Flat Package (eQFP)
eQFP is a term sometimes used to refer to QFP packages that incorporate enhancements or specific features beyond the standard configuration. These enhancements could include better thermal management, improved electrical performance, or other specialized characteristics.
-
Plastic Leaded Chip Carrier (PLCC)
While not strictly a QFP, PLCC is a related package type with a similar flat shape. It has leads that extend from all four sides, but they are arranged differently than in QFP.
The spacing of pins on a QFP can vary, as you mentioned, ranging from 0.4mm to 1mm apart. The specific type of QFP selected depends on factors such as space constraints, thermal considerations, and other requirements of the application.
Function of QFP
The Quad Flat Package (QFP) serves as a crucial component in the world of integrated circuits, offering a protective enclosure for ICs while establishing high-density electrical connections between the IC and the printed circuit board (PCB). Designed for surface mount technology (SMT), QFP's flat profile and numerous gull-wing leads enable efficient and automated assembly processes, contributing to space efficiency on the PCB. With its versatility, heat dissipation capabilities, and adaptability to various electronic applications, QFP has become a widely adopted packaging solution for integrated circuits requiring a significant number of interconnections within electronic circuits.
More Videos
Read More:
7404 Integrated Circuit (IC): Datasheet, Pinout, Pin Diagram, Truth Table
7408 Integrated Circuit Datasheet: Pinout, Pin Diagram, Truth Table
Photonic Integrated Circuit: Definition, Disadvantage, Fabrication, Application
IC 74192 UP/Down Counter Datasheet PDF, Circuit, Pin Diagram
IC 74190 Datasheet, Working, Features, Application
CD4017BE CMOS Counter: Circuit, Pinout and Uses [Datasheet PDF]
IC 7490 Decade Counter Datasheet: Features, Pinout, Circuit and Working
What is Integrated Circuit Design?- How to Design?
Hybrid Integrated Circuits (Hybrid IC): Definition, Examples, Uses & Advantages
How Is a Microprocessor Different From an Integrated Circuit
Small Outline Integrated Circuit - SOIC
Extended Reading
 FAQ
FAQ
-
What is the use of the QFN package?
Quad Flat No-Lead (QFN) packages exhibit versatility in diverse electronic systems. Air cavity QFNs are tailored for microwave applications operating between 20 to 25 GHz, meeting the stringent demands of high-frequency environments. In contrast, plastic molded QFNs, comprising a plastic compound and copper lead frame, offer a cost-effective alternative and find application in the 2-3 GHz frequency range.
-
What is the difference between DIP and QFP?
DIP packages, characterized by their larger size and low-density design, are primarily used for through-hole mounting. On the other hand, SOIC packages are smaller and intended for surface mounting. QFP packages share similarities with SOIC but offer a higher pin density, making them suitable for higher-performance circuits.
-
What is LQFP100?
LQFP100 is a Low Profile Quad Flat Package featuring 100 leads arranged with a 0.5 mm pitch. The package is characterized by a compact body measuring 14 mm by 14 mm, with a thickness of 1.4 mm.
-
What size is the LQFP?
Low Profile Quad Flat Package (LQFP) components come in various sizes to accommodate different applications and requirements. The body sizes of LQFP components typically range from 7 x 7mm to 28 x 28mm. These dimensions refer to the length and width of the component body. Additionally, LQFP components offer a variety of lead pitches, which is the distance between the centers of adjacent leads. Common lead pitches available for LQFP packages include 0.4mm, 0.5mm, 0.65mm, and 0.8mm.
-
What is the full form of the QFP package?
Quad Flat Packages (QFP)
-
What are the disadvantages of the QFN package
Quad Flat No-Lead (QFN) packages offer advantages like a compact design and simplified manufacturing, but they come with drawbacks. Oxidation issues in high humidity can compromise solderability, close pad proximity hampers precise soldering during rework, and the absence of leads may lead to floatation problems during solder reflow, affecting joint reliability. Additionally, the manufacturing complexity of flip-chip QFNs can raise costs. Careful consideration and mitigation strategies are crucial when using QFN packages in electronic designs.
-
What is the difference between QFP and LQFP packages
LQFP/TQFP is specifically designed to be thinner than standard QFP, contributing to reduced product thickness and increased board density. This thinner profile is advantageous for applications where height and weight are critical factors, leading to more portable end products.
Popular Blogs
-
Small Outline Packag...
SOP (Small Outline Package) is a type of integra...
-

CD4440 IC: Datasheet...
The CD4440 IC is a stereo audio power amplifier ...
-
Advantages and Disad...
Operational amplifiers, or op-amps, offer a host...
-

Dual Inline Package ...
Dual in-line package, also known as DIP package ...
Hot Products
-
-

-

-
-
-
-

-

-

-

-

-

-

-

-

-

-
-

-

-
-
-
-
-

-

-

-

-

Infineon Technologies Corporation
100V Single N-Channel HEXFET Power MOSFET in a PQF...
-

Infineon Technologies Corporation
100V Single N-Channel HEXFET Power MOSFET in a D2-...
-
Infineon Technologies Corporation
150V Single N-Channel HEXFET Power MOSFET in a 5mm...
-

Infineon Technologies Corporation
150V Single N-Channel HEXFET Power MOSFET in a D2-...
-

Infineon Technologies Corporation
200V Single N-Channel HEXFET Power MOSFET in a D2-...
-

-

Infineon Technologies Corporation
250V Single N-Channel HEXFET Power MOSFET PDP Swit...
-

-
-

-
-

Infineon Technologies Corporation
60V Single N-Channel HEXFET Power MOSFET in a PQFN...
-

Infineon Technologies Corporation
A 30V Single N-Channel HEXFET Power MOSFET in a Di...
-
-
-

-
-
-
-
-
-
-









