Dual Inline Package Meaning
Update Time: May 17, 2023 Readership: 4587
Contents
What is Dual Inline Package (DIP)?
Dual in-line package, also known as DIP package or DIP packaging, referred to as DIP or DIL, is a packaging method for integrated circuits, which are rectangular in shape and have two parallel rows of metal pins on either side of them, called row pins. Inserted in the DIP socket.
DIP packaged components are generally referred to as DIPn, where n is the number of pins, for example, the fourteen-pin integrated circuit is called DIP14, the overview figure is the DIP14 integrated circuit.
History of Dip Packaging
DIP was introduced in the 1970s and was a mainstay for a decade before the introduction of surface mount technology. DIP uses a plastic enclosure around the actual semiconductor and has two parallel rows of protruding electrical pins, called leadframes, that connect to the PCB (printed circuit board) below.
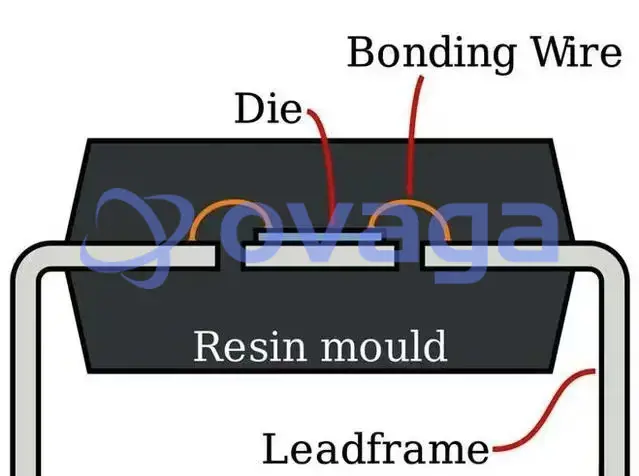
The actual die is then connected via bonding wires to two leadframes that can be connected to a printed circuit board (PCB).
Like many early semiconductor inventions, the DIP was created by Fairchild semi in 1964. the DIP package is a retro iconic design and the design choice is understandable. The actual die will be completely sealed with resin, resulting in high reliability and low cost, and many of the earliest iconic semiconductors were packaged in this manner. Note that the die is connected to an external lead frame via wires, making it a "lead bonding" packaging method.
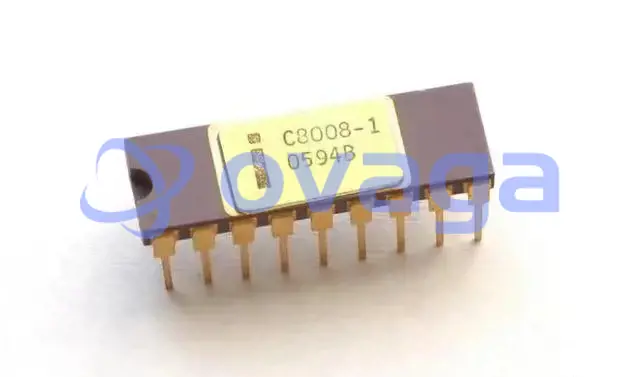
Here is the Intel 8008 - actually one of the first modern microprocessors. Note that it is in the iconic DIP package. So if you see those funky pictures of semiconductors that look like little spiders, that means it's a DIP package class semiconductor.
Different Structural Forms of Dip Packaging
- Multi-layer ceramic double in-line DIP
- Single-layer ceramic double in-line DIP
- Leadframe DIP (including glass-ceramic sealed type, plastic encapsulated structure type, ceramic low melt glass package type)
Number of Pins and Spacing
Commonly used DIP packages comply with JEDEC standards, the spacing between the two pins (pin spacing) is 0.1 inches (2.54 mm). The distance between the two rows of pins (row spacing, row spacing) depends on the number of pins, the most common being 0.3" (7.62 mm) or 0.6" (15.24 mm). Other less common distances are 0.4" (10.16 mm) or 0.9" (22.86 mm), and some packages are 0.07" (1.778 mm) between pins, and 0.3", 0.6" or 0.75" between rows.
The DIP packages used in the former Soviet Union and Eastern European countries are roughly close to the JEDEC standard, but the pin spacing uses the metric system of 2.5 mm instead of the 0.1" (2.54 mm) from the imperial system.
The number of pins in a DIP package is always an even number. If the line spacing is 0.3", a pin count of 8 to 24 is common, and occasionally you will see packages with a pin count of 4 or 28. If the line spacing is 0.6", the common pin counts are 24, 28, 32 or 40, and packages with pin counts of 36, 48 or 52 are also available. CPUs such as the Motorola 68000 and Zilog Z180 have a pin count of 64, which is the maximum number of pins for common DIP packages.

Orientation and Pin Numbering
When the component is identified with the notch facing up, the topmost pin on the left is pin 1, and the other pins are numbered in counterclockwise order. Sometimes pin 1 will also be marked with a dot.
For example, for DIP14 IC, when the identification notch is facing up, the pins on the left side are pins 1 to 7 in order from top to bottom, while the pins on the right side are pins 8 to 14 in order from bottom to top.
Advantages of DIP
- Ease of soldering: The through-hole mounting technology makes DIP packages relatively easy to solder manually or with automated processes.
- Accessibility: The pins of DIP packages are readily accessible, allowing for easy testing, troubleshooting, and socketing.
- Reliability: DIP packages offer a secure mechanical connection due to the through-hole mounting, making them resistant to mechanical stress and vibration.
Features
It is suitable for soldering through holes on PCB (printed circuit board) and easy to operate.
The ratio between chip area and package area is larger, so the volume is also larger.
The earliest CPUs such as the 4004, 8008, 8086, and 8088 all used the DIP package, which could be inserted into a slot on the motherboard or soldered to the motherboard through the two rows of pins on it.
DIP is also a derivative of SDIP (Shrink DIP), which has a six times higher pin density than DIP.
DIP is also short for dip switch, and its electrical characteristics are:
1. electrical life: each switch in the voltage 24VDC and current 25mA under the test, can be toggled back and forth 2000 times;;
2. The switch does not often switch the rated current: 100mA, withstand voltage 50VDC;
3. Switch often switch the rated current: 25mA, 24VDC;
4. contact impedance: (a) the initial value of the maximum 50mΩ; (b) the maximum value of 100mΩ after testing; 5. insulation impedance: minimum 100mΩ, 500VDC;
6. Withstand voltage strength: 500VAC / 1 minute;
7. inter-pole capacitance: maximum 5pF;;
8. circuit: single contact single selection: DS (S), DP (L).
In addition, the digital aspect of the film
DIP (Digital Image Processor) secondary actual image

Applications of DIP
Integrated circuits often use DIP packaging, other commonly used DIP packaging parts include DIP switches, LEDs, seven-segment displays, strip displays and relays. Computer and other electronic devices are also commonly used DIP-packaged connectors for the liner.
The earliest DIP packaging components were invented by Bryant Buck Rogers of Quick Semiconductor in 1964, the first component with 14 pins, quite similar to today's DIP packaging components. Its shape is rectangular, compared to earlier round components, rectangular components can increase the density of components in the board. dip packaging components are also very suitable for automated assembly equipment, the board can have dozens to hundreds of ICs, the use of wave soldering machine to weld all the parts, and then tested by automatic test equipment, only a few manual work. dip components are actually larger than their internal The size of DIP components is actually much larger than the integrated circuits inside them. At the end of the 20th century, surface mount technology (SMT) packaged components could reduce the size and weight of the system. However, there are still some occasions where DIP components are used, for example, when prototyping circuits, DIP components are used with breadboards to create circuit prototypes for easy insertion and removal of components.
Extended Reading
 FAQ
FAQ
-
Can DIP components be replaced with surface mount components?
In some cases, DIP components can be replaced with surface mount equivalents or adapters that convert DIP to SMT. However, this may require careful consideration of pin compatibility, electrical characteristics, and potential redesign of the circuit board. It is recommended to consult datasheets, component manufacturers, or design experts for proper guidance when considering component replacements.
-
Are there different sizes or variations of DIP packages?
Yes, DIP packages come in various sizes and pin configurations. Common variations include Dual Inline Package-16, Dual Inline Package-28, and Dual Inline Package-40, among others. The number after DIP indicates the number of pins in the package.
-
Are DIP packages still commonly used today?
While DIP packages have been widely used in the past, they are less common in modern electronics due to the popularity of surface mount technology (SMT). SMT offers smaller form factors, higher component density, and automated assembly advantages. However, DIP packages are still used in certain applications, particularly for legacy or specialized components.
Popular Blogs
-
Small Outline Packag...
SOP (Small Outline Package) is a type of integra...
-

CD4440 IC: Datasheet...
The CD4440 IC is a stereo audio power amplifier ...
-
Advantages and Disad...
Operational amplifiers, or op-amps, offer a host...
-

Dual Inline Package ...
Dual in-line package, also known as DIP package ...
Hot Products
-
-

-

-
-
-
-

-

-

-

-

-

-

-

-

-

-
-

-

-
-
-
-
-

-

-

-

-

Infineon Technologies Corporation
100V Single N-Channel HEXFET Power MOSFET in a PQF...
-

Infineon Technologies Corporation
100V Single N-Channel HEXFET Power MOSFET in a D2-...
-
Infineon Technologies Corporation
150V Single N-Channel HEXFET Power MOSFET in a 5mm...
-

Infineon Technologies Corporation
150V Single N-Channel HEXFET Power MOSFET in a D2-...
-

Infineon Technologies Corporation
200V Single N-Channel HEXFET Power MOSFET in a D2-...
-

-

Infineon Technologies Corporation
250V Single N-Channel HEXFET Power MOSFET PDP Swit...
-

-
-

-
-

Infineon Technologies Corporation
60V Single N-Channel HEXFET Power MOSFET in a PQFN...
-

Infineon Technologies Corporation
A 30V Single N-Channel HEXFET Power MOSFET in a Di...
-
-
-

-
-
-
-
-
-
-









