C1815 Transistor Datasheet, Pinout, Equivalent, Voltage, Circuit and Uses
Update Time: May 22, 2023 Readership: 14695
Contents
C1815 transistors are an integral part of many electronic devices and circuits. Known as the building blocks of modern electronics, transistors have played an important role in shaping the digital age. Among the huge transistor market, C1815 stands out for its special characteristics and has become a popular choice among the public.
In this article, we will explore the C1815 transistor in detail, delving into its datasheet to understand the technical specifications that define its capabilities. In addition, we will examine its pin configuration to help you identify the base, collector and emitter - essential knowledge for anyone planning to incorporate this transistor into their projects.
It is worth noting that C1815 and 2SC1815 transistors are essentially the same component. The prefix "2S" is usually added in accordance with the Japanese Industrial Standards (JIS) designation for semiconductors. Thus, "2SC1815" is the full JIS designation, while "C1815" is the abbreviation often used in practice. Both denote the same NPN transistor designed for audio frequency amplification and high voltage applications, recognized for low noise operation and excellent hFE linearity.
What is C1815 Transistor?
C1815 is a transistor that is a basic component used in electronic devices. This particular transistor is of the NPN (negative-positive-negative) type, referring to the configuration of the doping layer and the power of the carriers passing through it. c1815 transistors act as electronic switches and amplifiers. They control the flow of current through different circuit paths, depending on the input voltage or current.
In short, the C1815 transistor is a versatile electronic component used primarily in audio frequency amplification and high voltage applications, providing both low noise operation and excellent hFE linearity.
C1815 Transistor Voltage
The collector-base voltage (often denoted as V_CBO) of a C1815 transistor is a key parameter that indicates the maximum voltage the transistor can withstand between its collector and base terminals. In the case of the C1815, with a collector-base voltage rating of 50V, it means that you should not apply a voltage greater than 50 volts across the collector and base terminals in your circuit.
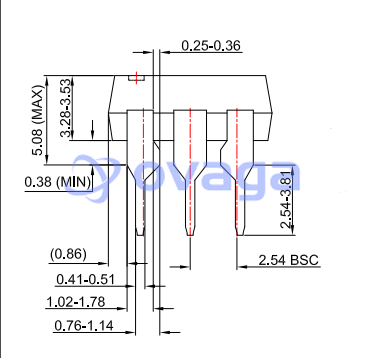
C1815 Pinout
The C1815 transistor, like most transistors, has three pins: base (B), collector (C), and emitter (E). Here is the pinout diagram for the C1815 transistor:
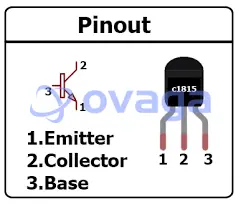
Pin Description:
Emitter (E): This terminal provides the main current flow path along with the collector. It is usually connected to a negative or ground voltage.
Collector (C): This terminal is involved in the main current flow and is controlled by the base. The collector is usually connected to a positive voltage.
Base (B): This is the control terminal of the transistor. A small current applied to the base controls the flow of a large current from the collector to the emitter.
C1815 Transistor Amplifier Circuit Diagram
C1815 and A1015 Audio Amplifier
audio amplifier with C1815
C1815 Features
Type: NPN transistor, mainly using electrons as charge carriers.
High Voltage: Can handle high voltages, typically a maximum collector-emitter voltage (Vce) of 50V and a maximum collector-base voltage (Vcb) of 60V.
Low noise: It is known for its low noise operation, which makes it ideal for audio amplification applications where noise can significantly degrade the quality of the output.
Good hFE linearity: The C1815 exhibits good hFE (DC current gain) linearity, which means that the gain varies minimally with the input current. This feature makes it popular in applications where precise amplification is required.
Collector current: Very high collector current of about 150mA.
Transition frequency: High transition frequency (typically 80MHz), which means it can operate effectively at high frequencies.
C1815 Datasheet
The definition and basic characteristics of the C1815 transistor have been generally described above, you can also browse this C1815 Transistor Datasheet to get detailed information about it, including Absolute Maximum Ratings, Electrical Characteristics table, etc.
C1815 vs 2N2222
The C1815 and 2N2222 are both NPN bipolar junction transistors (BJTs), but they have some differences in their electrical characteristics.
- Polarity
Both transistors are NPN, meaning they have an N-type semiconductor material for the majority carrier and P-type for the minority carrier. - Maximum Ratings
The maximum collector-base voltage (V_CBO) for the C1815 is typically around 50V, while the 2N2222 can handle higher voltages, typically up to 75V. - Current Ratings
The collector current (I_C) for the C1815 is usually in the range of 150mA, whereas the 2N2222 can handle higher collector currents, often up to 800mA. - Gain (hfe)
The current gain, represented by hfe, may vary between different batches or manufacturers, but in general, the 2N2222 tends to have a higher gain compared to the C1815. - Application
Both transistors can be used in general-purpose amplification and switching applications. However, due to differences in their electrical characteristics, one might be more suitable than the other for specific applications. - Pinout
While the pinout (the arrangement of the collector, base, and emitter terminals) is different between the C1815 and 2N2222, it's a mechanical difference and can be accommodated in circuit design.
C1815 Uses
The C1815 is a highly versatile transistor known for its use in a variety of applications in electronics. Its low noise and excellent hFE linearity make it ideal for audio amplification circuits and is commonly used in audio equipment for preamplifier stages, audio power amplifiers and signal amplification.
In addition, its switching capability allows it to efficiently control the operation of other components or circuits. c1815 also has important uses in signal processing tasks, including signal amplification, filtering and modulation, as well as in radio frequency (RF) applications due to its high conversion frequency. In addition, its powerful high voltage and current handling characteristics make it a suitable component in power conditioning and DC-DC conversion circuits. Due to their wide availability and versatility, C1815 transistors are also very popular in DIY electronics projects, learning kits and prototyping.
C1815 vs BC547
The C1815 and BC547 are both NPN bipolar junction transistors (BJTs) commonly used for amplification and switching purposes.
Polarity
Both transistors are NPN, meaning they have an N-type semiconductor material for the majority carrier and P-type for the minority carrier.
Maximum Ratings
The maximum collector-base voltage (V_CBO) for the C1815 is typically around 50V, while the BC547 has a V_CBO of around 80V. The BC547 can handle a higher maximum voltage.
Current Ratings
The collector current (I_C) for the C1815 is usually in the range of 150mA, while the BC547 has a similar collector current rating.
Gain (hfe)
The current gain, represented by hfe, may vary between different batches or manufacturers. In general, the BC547 and C1815 have comparable gain values, though specific values can vary.
Application
Both transistors are suitable for general-purpose amplification and switching applications. They are often used in low to moderate power circuits.
Pinout
The pinout (arrangement of collector, base, and emitter terminals) is different between the C1815 and BC547, but this is a mechanical difference that can be accommodated in circuit design.
C1815 Pros and Cons
The main advantage of the C1815 transistor is its ability to operate at low noise levels, a feature that makes it well suited for use in audio amplification circuits. Its excellent hFE linearity also ensures accurate amplification and faithful signal reproduction, which is essential for high-quality audio output. In addition, it can handle high voltages and sizable collector currents and apply them to power conditioning circuits. the C1815's high conversion frequency also allows it to operate efficiently at high frequencies, thus expanding its use in RF applications.
However, as with any electronic component, the C1815 transistor has some limitations. Despite its high voltage handling capability, it is not suitable for very high power applications due to its limited power dissipation capability. In addition, while it performs very well in audio frequency applications, it may not be optimal for circuits that require extremely high speed switching or very high frequency operation that exceeds its transition frequency limits. It is also worth noting that while the C1815 is widely available, sometimes component shortages or regional availability may necessitate the use of equivalent transistors. Therefore, it is important to consider the advantages and disadvantages of the C1815 when selecting it for a particular application.
C1815 Transistor Equivalent /Substitute/ Replacement
The C1815 transistor has several equivalent parts that can be used as replacements if the C1815 is not available or is not suitable for a particular application. These equivalent parts have similar electrical characteristics and can perform similar functions in most circuits. The following are a few equivalent parts for the C1815 transistor:
2N5088: A general purpose NPN transistor known for its low noise and high gain for audio and general purpose amplification.
BC549: A low-noise, low-signal NPN BJT transistor typically used in audio amplifiers.
BC107: A general purpose NPN transistor for low power audio applications.
2N2222: A widely used NPN transistor known for its versatility and ruggedness.
BC547: Another popular NPN transistor used for general purpose switching and amplification.
C945 vs C1815
The C945 and C1815 are both NPN bipolar junction transistors (BJTs), but they have some differences in their electrical characteristics.
Collector-Base Voltage (V_CBO)
The C945 typically has a lower collector-base voltage (V_CBO) rating, often around 60V, while the C1815 is typically rated at 50V.
Collector Current (I_C)
The collector current (I_C) for the C945 is usually in the range of 150mA, similar to the C1815.
Gain (hfe)
The current gain, represented by hfe, may vary between different batches or manufacturers. Generally, both transistors have comparable gain values, though specific values can vary.
Application
Both transistors are commonly used for general-purpose amplification and switching applications, especially in low to moderate power circuits.
Pinout
The pinout (arrangement of collector, base, and emitter terminals) is different between the C945 and C1815. It's essential to refer to the datasheets to ensure the correct connection in your circuit.
C1815 Transistor Projects
How to Test C1815 Transistor (C1815 Transistor Testing)
C1815 PNP Complementary
The C1815 and A1015 transistors are complementary pairs, meaning one is NPN (C1815), and the other is PNP (A1015). Complementary pairs of transistors are often used in electronic circuits to design push-pull amplifiers, which can be beneficial for applications like audio amplification.
C1815:
NPN bipolar junction transistor (BJT).
Commonly used for amplification and switching applications.
The collector-base voltage (V_CBO) is typically around 50V.
Maximum collector current (I_C) is typically around 150mA.
A1015 (2SA1015):
PNP bipolar junction transistor (BJT).
Similar to the C1815, it is used for amplification and switching.
The collector-base voltage (V_CBO) is typically around 50V.
Maximum collector current (I_C) is typically around 150mA.
When using these transistors in complementary configurations, it's important to consider their specific characteristics, such as gain (hfe), voltage ratings, and current ratings.
Related Parts
C1815 GR331
C1815 SMD
C1815GR
C1815Y
C1815 GR011
C1815 SOT23
BR C1815
C1815 CR331
C1815L
Conclusion
In summary, the unique characteristics of the C1815 transistor make it highly useful for audio frequency amplification and high voltage applications. This article reveals the wide range of potential this component brings through an in-depth discussion of its data sheet, pinout, equivalent components, and various uses. Hopefully, with this knowledge gained, you will be able to effectively harness the power of the C1815 transistor in your next electronics project, opening up new possibilities in your journey through the world of electronics.
Extended Reading
 FAQ
FAQ
-
Can the C1815 transistor be used for DIY electronic projects?
Yes, the C1815 is often used by hobbyists and students for DIY electronic projects, learning kits, and prototyping due to its wide availability, versatility, and robust characteristics.
-
Are there any limitations to using the C1815 transistor?
While the C1815 is a versatile transistor, it may not be suitable for extremely high-power applications due to its limited power dissipation capacity. It may also not be the best fit for circuits that require extremely high-speed switching or very high frequency operation beyond its transition frequency limit.
-
Is the C1815 transistor suitable for audio amplification?
Yes, the C1815 is often used in audio amplification circuits due to its low noise operation and excellent hFE linearity, making it ideal for high-quality audio output.
-
What is the maximum collector current for the C1815 transistor?
The C1815 transistor typically has a maximum collector current of about 150mA.
Popular Blogs
-

PCA9617ADPJ Datashee...
The PCA9617ADPJ is a signal buffer and repeater ...
-
D882 Transistor Pino...
The D882 transistor is a commonly used NPN bipol...
-
C1815 Transistor Dat...
The C1815 is a general purpose NPN transistor us...
-

C945 Transistor Data...
The C945 transistor is a small, low-power NPN bi...