LR44 vs 357: Are LR44 and 357 Batteries the Same
Update Time: Nov 20, 2023 Readership: 4242
Contents
In button cell batteries, the LR44 and 357 have emerged as popular choices. Are LR44 and 357 batteries essentially the same, or do their specifications and applications reveal nuances? This article seeks to unravel the similarities and differences between LR44 and 357 batteries, shedding light on their chemistry, voltage characteristics, applications, and more.
Overview of LR44
The LR44 battery, an alkaline button cell, stands out for its versatile application in a diverse range of devices. With a nominal voltage of 1.5 volts and dimensions measuring 5.4mm in diameter and 11.6mm in height, it offers a relatively high energy density. This battery type is commonly found in small electronic gadgets, watches, calculators, and medical devices. Users should be mindful of its voltage decay characteristics, as the output steadily drops during discharge, and some devices may exhibit reliability concerns if the voltage falls below a specific threshold. Despite its widespread use, the LR44's taller height may impact its fit in certain battery compartments, making compatibility considerations important.
Specifications
|
Characteristic |
LR44 |
|
Battery Type |
Alkaline Manganese Batteries |
|
Nominal Voltage |
1.5V |
|
Nominal Capacity |
120mAh |
|
Operating Temperature Range |
-10℃ to 60℃ |
|
Diameter (inch) |
0.457inch |
|
Diameter (mm) |
11.6mm |
|
Height (inch) |
0.213inch |
|
Height (mm) |
5.4mm |
|
IEC (JIS) |
LR44 |
|
Mass (oz) |
0.0705oz |
|
Mass (g) |
2g |
LR44 Battery Equivalent parts
AG13: AG13 is a common equivalent for LR44. It has the same size and voltage, making it a suitable replacement.
A76: A76 is another designation that is equivalent to LR44. It shares the same size and voltage specifications.
357: The 357 battery, also known as SR44, is often considered interchangeable with LR44 due to similar size and voltage.
SR44: SR44 is another designation that is equivalent to LR44. It has the same size and voltage and is often used interchangeably.
G13: G13 is another alternative designation for LR44. It shares the same size and voltage characteristics.
PX76A: PX76A is yet another equivalent for LR44, often used in photography equipment.
Overview of 357
The 357 battery, classified as a silver oxide cell, is distinguished by its reliable performance in precision devices. With a nominal voltage of 1.55 volts and a capacity typically around 150mAh, the 357 exhibits a stable and consistent voltage output throughout its lifespan, making it an ideal power source for watches, calculators, toys, and various medical instruments. Notable for its longer lifespan, ranging from 30% to 100% more than an LR44 battery, the 357 provides extended operational life and reduces the frequency of battery replacements. Its compact dimensions, measuring 11.6mm in diameter and 5.4mm in height, contribute to its compatibility in various battery compartments.
Specifications
|
Characteristic |
357 |
|
Battery Type |
Silver Oxide |
|
Nominal Voltage |
1.55V |
|
Nominal Capacity |
150mAh |
|
Operating Temperature Range |
-28C to 55 C |
|
Diameter (inch) |
0.457inch |
|
Diameter (mm) |
11.6mm |
|
Height (inch) |
0.213inch |
|
Height (mm) |
5.4mm |
|
IEC (JIS) |
|
|
Mass (oz) |
|
|
Mass (g) |
2.3g |
357 Battery Equivalent Parts
SR44: SR44 is one of the most common equivalents for the 357 battery. It shares the same size and voltage specifications.
AG13: AG13 is another equivalent for the 357 battery. Like SR44, it has the same size and voltage and is often used interchangeably.
A76: A76 is a designation that is equivalent to 357. It shares the same size and voltage characteristics.
SG13: SG13 is another alternative designation for the 357 battery. It has the same size and voltage.
PX76A: PX76A is yet another equivalent for the 357 battery, often used in photography equipment.
Button Battery: LR44 vs 357
LR44 vs. 357 Batteries Catalog:
Chemistry Differences
Voltage Differences
Voltage Decay Differences
Lifespan Differences
Size Differences
Cost Differences
Conclusion (Comparison Table)
Chemistry Differences: LR44 (Alkaline) vs. 357 (Silver Oxide)
-
Alkaline LR44 Battery
LR44 batteries use alkaline chemistry. Alkaline batteries typically contain zinc and manganese dioxide as the primary components.
Performance Characteristics:
Alkaline chemistry provides a relatively high energy density.
Voltage output starts to drop steadily as the battery discharges.
Suitable for a wide range of applications with varying power demands.
Common Applications:
LR44 batteries are commonly used in devices such as small electronic gadgets, watches, calculators, and medical devices.
-
Silver-Oxide 357 Battery
357 batteries utilize silver oxide chemistry. Silver oxide batteries contain silver oxide as the positive electrode, zinc as the negative electrode, and an alkaline electrolyte.
Performance Characteristics:
Silver oxide chemistry offers a stable and relatively constant voltage output throughout the majority of the battery's life.
Higher energy density compared to alkaline batteries, making them suitable for devices with precision requirements.
Typically used in applications demanding a consistent and reliable power source, such as watches and medical instruments.
Common Applications:
357 batteries are commonly found in watches, calculators, toys, and various medical devices.
- Considerations for Choosing Between LR44 and 357:
Voltage Stability: The silver oxide chemistry of 357 batteries provides a more stable voltage output, making them preferable for precision devices.
Energy Density: Silver oxide batteries often have a higher energy density, allowing them to power devices with higher energy demands.
Voltage: LR44 vs. 357 Batteries
LR44 is rated at 1.5v, while 357 is rated at 1.55v.
1. Device Compatibility:
LR44 Batteries:
Suitable for devices that can operate within a 1.5-volt power supply.
Widely used in various electronic gadgets, watches, calculators, and medical devices.
357 Batteries:
Ideal for devices that require a slightly higher voltage of 1.55 volts.
Commonly found in precision instruments like watches, calculators, and medical devices.
2. Voltage Stability:
LR44 Batteries:
Output voltage starts to drop steadily as the battery discharges.
May be suitable for devices where a gradual decrease in voltage is acceptable.
357 Batteries:
Silver oxide chemistry provides a stable and relatively constant voltage output throughout most of the battery's life.
Beneficial for precision devices that require a consistent power supply.
3. Sensitivity to Voltage:
LR44 Batteries:
Some devices may experience reliability concerns if the battery voltage falls below a certain threshold (e.g., 1.2 volts).
357 Batteries:
Preferred for applications with specific voltage requirements, such as watches, where constant and precise voltage is crucial for accurate timekeeping.
4. Energy Density:
LR44 Batteries:
Provide a relatively high energy density at 1.5 volts, suitable for various applications.
357 Batteries:
Higher rated voltage (1.55 volts) contributes to a potentially higher energy density, making them suitable for devices with higher energy demands.
Understanding the voltage differences between LR44 and 357 batteries is essential for selecting the appropriate battery for specific devices. The slightly higher voltage of the 357 battery, along with its stable output, makes it particularly well-suited for precision instruments and applications with specific voltage requirements. It's crucial to consider the voltage sensitivity of the device and choose the battery accordingly for optimal performance.
Voltage Decay
The silver oxide 357 maintains a more constant voltage until the end of its life at 1.2v, while the alkaline LR44 drops to 1.0v.
1. Alkaline LR44 Battery:
Voltage Decay Characteristics:
As the LR44 battery discharges, the voltage output exhibits a gradual and more linear decline.
The voltage may drop to 1.0 volts or below as the battery approaches the end of its life.
Implications:
Devices powered by LR44 batteries may experience a relatively steady decrease in voltage, potentially impacting performance in applications sensitive to voltage fluctuations.
Some devices may have a cutoff threshold, below which reliability concerns arise.
2. Silver Oxide 357 Battery:
Voltage Decay Characteristics:
The silver oxide chemistry in 357 batteries allows for a more constant voltage output throughout the majority of the battery's life.
The voltage remains stable until the end, at which point it may drop to 1.2 volts.
Implications:
Devices powered by 357 batteries benefit from a more stable and consistent voltage supply.
Precision instruments, such as watches, calculators, and medical devices, can maintain accurate functionality until the battery is near depletion.
Considerations and Applications:
-
Precision Devices
LR44 Batteries:
Suitable for devices where a gradual decline in voltage is acceptable.
May be used in applications with lower precision requirements.
357 Batteries:
Ideal for precision instruments that demand a stable and constant voltage supply.
Commonly used in watches and medical devices where accuracy is crucial.
-
Device Reliability
LR44 Batteries:
Reliability concerns may arise in devices that are sensitive to voltage drops below a certain threshold, such as 1.0 volts.
357 Batteries:
The more constant voltage output contributes to consistent device performance, enhancing reliability.
-
End-of-Life Voltage:
LR44 Batteries:
Voltage may drop to 1.0 volts or lower, indicating the end of its usable life.
357 Batteries:
Maintains a stable voltage until the end, with a drop to 1.2 volts, providing longer and more predictable functionality.
Understanding the voltage decay characteristics is crucial for selecting the appropriate battery for specific applications, especially those requiring precision and reliability. The choice between LR44 and 357 batteries should align with the voltage requirements and sensitivity of the devices they power.
Lifespan: LR44 vs. 357 Batteries
1. Alkaline LR44 Battery:
Lifespan Characteristics:
The lifespan of LR44 batteries is influenced by factors such as discharge rate, usage patterns, and the specific requirements of the devices they power.
Average nominal capacity in the range of 110-130 mAh.
Implications:
Suitable for a variety of applications with moderate energy demands.
Performance may vary based on usage and device characteristics.
2. Silver Oxide 357 Battery:
Lifespan Characteristics:
The silver oxide chemistry in 357 batteries often provides a longer lifespan compared to LR44 batteries.
Higher nominal capacity, typically in the range of 150-200 mAh or even more, depending on discharge currents.
Implications:
Suitable for applications with higher energy demands and those requiring a more extended operational life.
Preferred for precision devices where a stable and reliable power source is crucial.
Percentage Difference in Lifespan:
The statement "357 typically lasts 30% to 100% longer than the LR44" implies a significant advantage in favor of the 357 battery.
Considerations and Applications:
-
High Energy Demand Devices:
LR44 Batteries:
Well-suited for devices with moderate energy demands.
357 Batteries:
Preferred for devices with higher energy demands due to their higher nominal capacity.
-
Precision Instruments:
LR44 Batteries:
Adequate for applications with lower precision requirements.
357 Batteries:
Ideal for precision instruments such as watches and medical devices where a longer lifespan and stable voltage are critical.
-
Impact on Frequency of Battery Replacement:
LR44 Batteries:
May require more frequent replacements in devices with higher energy demands.
357 Batteries:
Longer lifespan reduces the frequency of battery replacements, providing convenience and potentially reducing long-term costs.
-
Shelf Life
LR44 Batteries:
Average shelf life of around 3 years, with some newer versions offering extended shelf life (4-5 years).
357 Batteries:
Standard 357 models often have a 5-year shelf life, showcasing their longevity on the shelf.
Size: LR44 (Alkaline) vs. 357 (Silver Oxide) Batteries
1. Alkaline LR44 Battery:
Size Characteristics:
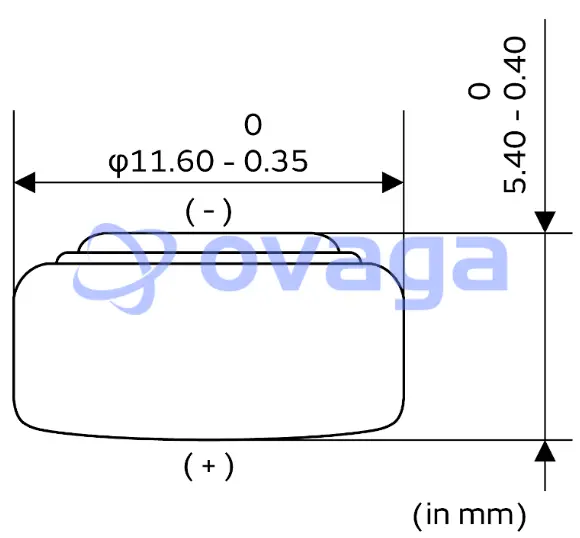
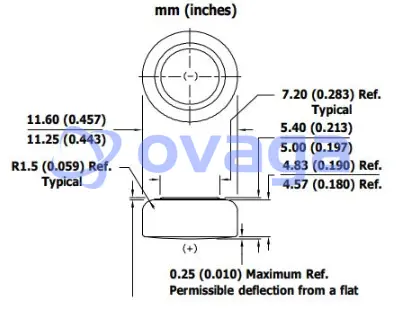
The LR44 battery typically has a specific size, commonly measured as 5.4mm in diameter and 11.6mm in height.
Its height is a defining factor, and it tends to be relatively taller compared to some other button cell batteries.
Implications:
The taller height of LR44 batteries may impact their fit in certain battery compartments, especially those designed for shorter batteries.
2. Silver Oxide 357 Battery:
Size Characteristics:
The 357 battery shares the same standard size dimensions, often measured as 5.4mm in diameter and 9.5mm to 9.6mm in height.
Its height is slightly shorter than that of the LR44 battery.
Implications:
The slightly shorter height of the 357 battery makes it more suitable for battery compartments with limited vertical space.
Considerations and Applications:
-
Device Compatibility:
LR44 Batteries:
May face challenges fitting into battery compartments designed for shorter batteries.
Compatibility depends on the specific design of the device and its battery compartment.
357 Batteries:
More likely to fit comfortably in a variety of battery compartments due to its slightly shorter height.
-
Compact Devices:
LR44 Batteries:
May pose challenges in ultra-compact devices with tightly designed battery compartments.
Taller height may limit its use in devices where space is a critical factor.
357 Batteries:
Well-suited for compact devices that require a button cell with standard dimensions.
-
Watch Batteries:
LR44 Batteries:
Compatibility may vary for watch battery compartments, depending on the specific watch design.
357 Batteries:
Often a preferred choice for watches and other precision instruments due to its standard size and slightly shorter height.
-
Impact on Consumer Convenience:
LR44 Batteries:
Consumers may need to be mindful of the height difference when replacing batteries, ensuring a proper fit in the device.
357 Batteries:
Generally offers more flexibility in terms of fitting into various battery compartments, contributing to consumer convenience.
Overall Compatibility:
Both LR44 and 357 batteries share the same diameter, making them physically compatible in many applications. However, the height difference is a critical factor in specific devices and should be considered when choosing between the two.
Cost
The cost consideration for both LR44 and 357 batteries highlights that they are not as economically advantageous as certain alternative battery types.
LR44 batteries, while offering good cost performance, are not as cost-effective when compared to some other battery types. Batteries like zinc carbon and certain silver oxide alternatives may provide a more budget-friendly option.
Similarly, 357 batteries also face the challenge of not being as cost-effective when compared to certain battery types. This includes zinc carbon batteries and specific silver oxide alternatives, which may be more economical choices for users seeking a balance between performance and cost.
Conclusion:
| Characteristic | LR44 (Alkaline) | 357 (Silver Oxide) |
| Chemistry | Alkaline | Silver Oxide |
| Voltage | 1.5V | 1.55V |
| Rechargeable | Typically non-rechargeable | Typically non-rechargeable |
| Capacity | Generally lower capacity |
Higher capacity (often 30% to 100% longer lifespan)
|
| Voltage Stability | Voltage drops steadily as it discharges | Relatively constant voltage output |
| Lifespan | Average lifespan with moderate energy demands |
Longer lifespan, suitable for higher energy demands
|
| Size | 5.4mm diameter, 11.6mm height (taller) | 5.4mm diameter, 9.5mm to 9.6mm height (shorter) |
| Common Applications | Various electronic gadgets, watches, calculators | Watches, calculators, toys, medical devices |
| Cost | Generally less expensive than 357 | Generally more expensive than LR44 |
Disadvantages of LR44 and 357
| Disadvantages | LR44 | 357 |
| Rechargeability | Not rechargeable | Not rechargeable |
| Capacity | Lower capacity compared to similar batteries | Capacity loss over time |
| Voltage | 1.5V | 1.55V |
| Heat Sensitivity | - | More sensitive to heat than alkaline batteries |
| Cost | Costly compared to some other batteries | Costly compared to some other batteries |
LR44 vs 357: Similarities
Size: LR44 and 357 batteries share identical external dimensions (5.4mm x 11.6mm).
Voltage and Size Compatibility: Despite differences, they are often considered interchangeable in some devices due to their close voltage and size.
Manufacturer Naming: Manufacturers often use different names for the same cell (LR1154, AG13, LR44, 357, A76), causing potential confusion for consumers.
External Dimensions and Voltage: The external dimensions and voltage are the same, making them physically compatible in many cases.
Device Compatibility: In devices specifying LR44/A76 cells, using 357s may offer longer useful life due to their higher capacity, but this depends on the specific requirements of the device.
Can a 357 or 303 Button Battery Safely Replace an LR44?
The interchangeability of button batteries like LR44, 357, and 303 depends on various factors, including size, voltage, and application requirements. In some cases, these batteries may be considered equivalent, but it's essential to understand the nuances.
-
Size Compatibility
LR44, 357, and 303 batteries often share the same physical dimensions, making them interchangeable in devices that accommodate these sizes.
-
Voltage Differences
LR44 is typically rated at 1.5 volts, while 357 and 303 batteries are often rated at 1.55 volts. Although the voltage difference is small, it could impact the performance of certain devices, especially those sensitive to voltage variations.
-
Chemistry Variations
LR44 is an alkaline battery, while 357 and 303 are often silver oxide batteries. The chemistry difference may affect the batteries' performance characteristics, such as discharge rate and overall lifespan.
-
Application Considerations
For low-drain applications, silver oxide batteries like 357 and 303 may provide longer life compared to LR44, which is more suitable for high-drain applications.
While Amazon may list LR44, 357, and 303 as equivalent, it's important to consider that general equivalency does not guarantee identical performance in all devices. Manufacturer recommendations should still be prioritized.
SR44 vs 357
| Characteristic | SR44 | 357 |
| Chemistry | Silver-oxide | Silver-oxide |
| Composition | Contains silver, zinc, silver oxide | Contains silver, zinc, silver oxide |
| Voltage | 1.55V | 1.55V |
| Rechargeable | Typically non-rechargeable | Typically non-rechargeable |
| Capacity | May have higher capacity | Varies, but often comparable to SR44 |
| Common Applications | Watches, cameras, electronics | Watches, cameras, electronics |
| Cost | Often more expensive | Generally less expensive compared to SR44 |
AG13 Battery vs 357
| Characteristic | AG13 | 357 |
| Other Names | LR44, A76 | SR44, SR1154 |
| Chemistry | Alkaline | Silver-oxide |
| Voltage | 1.5V | 1.55V |
| Rechargeable | Typically non-rechargeable | Typically non-rechargeable |
| Common Applications | Watches, calculators, electronics | Watches, cameras, electronics |
| Cost | Generally less expensive | Varies, but often more expensive than AG13 |
SR44 vs LR44
| Characteristic | SR44 | LR44 |
| Chemistry | Silver-oxide | Alkaline |
| Composition | Contains silver, zinc, silver oxide | Contains zinc, manganese dioxide |
| Voltage | 1.55V | 1.5V |
| Rechargeable | Typically non-rechargeable | Typically non-rechargeable |
| Capacity | May have higher capacity | Generally lower capacity |
| Common Applications | Watches, cameras, electronics | Watches, calculators, electronics |
| Cost | Often more expensive | Generally less expensive |
Final Words
While these button cells share commonalities in terms of size and external dimensions, their internal chemistry and performance characteristics set them apart. LR44, with its alkaline composition, caters to a range of devices with moderate energy demands, offering stable discharge and cost-effective performance. On the other hand, the 357, powered by silver oxide chemistry, stands out for its higher nominal voltage, longer lifespan, and suitability for precision instruments.
Read More:
CR2016 vs. CR2032: Is CR2016 Same as CR2032
LR44 VS SR44: Is SR44 the Same as LR44
CR1220 Battery Equivalent & Cross Reference Chart
Top Picks for LR44 Battery Equivalents
Extended Reading
 FAQ
FAQ
-
Do LR44 batteries have silver?
LR44 batteries typically do not contain silver and are commonly composed of alkaline chemistry with materials like zinc and manganese dioxide. On the other hand, SR44 batteries, which are based on silver-oxide chemistry, do contain silver along with zinc and silver oxide.
-
What battery can I use instead of LR44?
SR44 battery can be used as a replacement for the LR44 battery in many applications. While both batteries share the same physical size and shape (11.6mm diameter, 5.4mm height) and are often interchangeable, there are some differences in their chemistry and voltage. The LR44 battery is an alkaline battery with a nominal voltage of 1.5V, while the SR44 battery uses silver oxide chemistry and has a slightly higher nominal voltage of 1.55V. The voltage difference is minimal, and in many devices, the SR44 can effectively substitute for the LR44.
-
Is LR41 the same as 357?
The LR41 and 357 batteries are not the same; they differ in terms of size, chemistry, and voltage. The LR44 and 357 are indeed considered equivalents in many cases, but the LR41 is a different size and not equivalent to the 357.
-
What does LR stand for in batteries?
In the context of batteries, the LR designation typically indicates an Alkaline battery.
-
Is SR44 the same as 357?
Yes, SR44 is the same as 357 when it comes to button cell batteries. The SR44 is often interchangeable with the 357, and they share the same physical size and voltage specifications. Therefore, an SR44 battery can be used as a direct replacement for a 357 battery and vice versa.
-
At what voltage is a LR44 battery dead?
0.9-1.0 volts.
-
Can a 675 battery replace a LR44?
The LR44 and 675 batteries are not interchangeable due to differences in size and voltage. The LR44 is a smaller button cell battery commonly used in watches, calculators, and various small electronic devices, while the 675 battery is larger and typically used in hearing aids.
-
Can I use SR44 instead of LR44?
Yes, in many cases, you can use SR44 batteries as a substitute for LR44 batteries, and vice versa, because they share the same size and shape. Both batteries are button cell batteries commonly used in small electronic devices, watches, calculators, and other applications.
-
Is LR44 the same as 386?
While the LR44 and 386 batteries share similar sizes, they are different in terms of chemistry. The LR44 typically uses alkaline chemistry, while the 386 (and its equivalents) generally uses silver oxide chemistry. Additionally, the nominal voltage of an LR44 is 1.5V, while the 386 usually has a nominal voltage of 1.55V.
Popular Blogs
-

CR1220 Battery Equiv...
The CR1220 is a coin cell battery with a diamete...
-

CR2016 vs. CR2032: I...
CR2032 is used in electronic dictionaries, and C...
-

LR44 vs 357: Are LR4...
In button cell batteries, the LR44 and 357 have ...
-
Six TDA2822m Applica...
This article will introduce in detail six TDA282...














