What is Electronic Ballast?
Update Time: May 05, 2023 Readership: 3014
Contents
The Definition of Electronic Ballast
Electronic ballast is a kind of ballast, which refers to electronic equipment that uses electronic technology to drive electric light sources to produce the required lighting. Corresponding to it is the magnetic ballast (or ballast). More and more modern fluorescent lamps use electronic ballasts, which are light and compact, and can even integrate electronic ballasts with lamp tubes. Go for the starter alone. Electronic ballasts can also have more functions, such as improving or eliminating the flickering phenomenon of fluorescent lamps by increasing the current frequency or current waveform (such as becoming a square wave); it is also possible to use DC power for fluorescent lamps through the power inversion process. Some disadvantages of the traditional inductive rectifier make it being replaced by increasingly sophisticated electronic ballasts.
How to Distinguish the Quality of Electronic Ballasts
Remove the starter, disconnect the power supply, and test both ends of the ballast. If the ballast is of the older inductive type, the inductive type can use this method to test whether the coil is burnt out. This kind of old-fashioned ballast is broken, usually because the coil is blown, resulting in no voltage at both ends of the lamp tube, which will not cause the lamp tube to burn out. There are many situations for electronic ballasts.
You can measure the resistance values of the three ballasts according to the method mentioned above to see if there is a big difference, so as to judge whether the ballast is damaged. You can also change the starter to see if the burning starter can't be disconnected, and it's always in the ON state. In short, use the substitution method.
Working Principle of Electronic Ballast
Brief Description
In order for fluorescent lamps and germicidal lamps to work properly, three conditions must be met:
a. Filament preheating current or filament current
b. High voltage start c. Limit operating current

Specific Analysis
Working principle of electronic ballast Since gas discharge lamp (such as fluorescent lamp, neon lamp, metal halide lamp, etc.) is a negative resistance electric light source with V-I characteristics, that is, negative value, when the lamp current rises, the work of the lamp tube The voltage drops, but the power supply voltage will not drop. After the extra voltage is added to the lamp tube, the lamp current will rise further, and this cycle will eventually burn out the lamp tube or turn off the lamp tube. Therefore, to make the lamp tube work normally, it should be Equipped with ballast components to limit and stabilize lamp current. This current limiting device is called a ballast. There are two types of ballasts commonly used for gas discharge lamps: inductive ballasts and high-frequency AC electronic ballasts. Since the inductive ballast works at the frequency of the mains power, it is bulky and heavy, and consumes a lot of metal materials such as copper and silicon steel. It has difficulty in heat dissipation, low work efficiency, and flickering lights. Therefore, some technologies in the field of electric light sources Workers are looking for new ballast methods, and high-frequency AC electronic ballasts are an effective method.
In the circuit shown in Figure 1, the working voltage on the lamp tube plus the voltage on the ballast element is equal to the power supply voltage, which can finally make the gas discharge lamp work stably. In the circuit shown in Figure 1, the lamp power can be calculated as follows:
P=IVα (1)
α in the formula represents the luminous coefficient of the lamp, which is related to the working voltage and current of the lamp tube. For magnetic ballasts, α can be 0.8, and for high-frequency electronic ballasts, α can be 0.99.
During the stable operation of the lamp circuit, the voltage on the lamp tube is stable, so the lamp power mainly depends on the magnitude of the lamp current, and the magnitude of the lamp current is related to the impedance of the ballast element and the level of the power supply voltage, and the power supply frequency has a great influence on the power supply. The work of fluorescent lights also has an effect. For example, for inductive ballast, the impedance of the ballast inductance ZL=2πfL, the inductance of the inductance ballast is related to the number of winding turns and the size of the iron core, so when the power supply frequency is high, the volume of the ballast inductance will also increase smaller. This is the reason why the volume and size of the ballast inductor will be small after the high-frequency AC electronic ballast circuit is adopted.
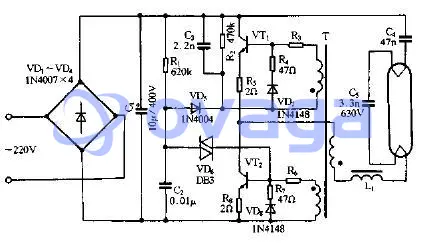
Figure 1: Electronic ballast circuit
Basic Classification
By Installation Mode
(1) Independent
(2) built-in
(3) Integral
According to Performance Characteristics
(1) Ordinary type, 0.6≥120%90%1.4~1.6 High frequency makes it small, light, and has power-saving function;
(2) High power factor type H class, ≥0.9≤30%≤18%1.7~2.1 Adopt passive filter and abnormal protection;
(3) High-performance electronic ballast L-class, ≥0.95≤20%≤10%1.4~1.7 has perfect abnormal protection function, electromagnetic compatibility;
(4) Class L electronic ballast with high cost performance, ≥0.97≤10%≤5%1.4~1.7 integrated technology and constant power circuit design, the voltage fluctuation has little influence on the illumination;
(5) Dimmable electronic ballasts, ≥0.96≤10%≤5%≤1.7 Adopt integrated technology and active variable frequency resonance technology.
Advantages of Electronic Ballast
(1) Energy saving. Electronic ballasts for fluorescent lamps use 20-60khz frequency to supply the lamp tubes, so that the light efficiency of the lamp tubes is about 10% higher than that of the power frequency (according to the lamp tubes with a length of 4 feet), and their own power consumption is low, so that the total power of the lamps The input power is reduced by about 20%, which has a better energy-saving effect.
(2) Eliminate strobe and make the light more stable. It is beneficial to improve visual resolution and improve efficacy; it can reduce visual fatigue of continuous operation and help protect eyesight.
(3) The starting point is more reliable. After preheating the lamp, the starting point was successful once, avoiding multiple starting points.
(4) High power factor. Fluorescent lamps above 25W that meet national standards have a power factor higher than 0.95. However, it should be noted that the national standard stipulates a high harmonic limit for lamps below 25W, so that the power factor drops to 0.7-0.8.
(5) Stable input power and output luminous flux: High-quality products have good voltage stabilization performance. When the power supply and voltage deviation are large, they can still maintain a constant power of the light source and stabilize the illuminance, which is conducive to energy saving.
(6) Extend the life of the lamp tube. Factors such as constant wattage and reduced lamp current for high-quality products, as well as reliable starting points, result in longer lamp life.
(7) Low noise. The noise of high-quality electronic ballasts can reach below 35db, and people can't feel the noise.
(8) Can be dimmed. For places that require dimming, such as places where incandescent lamps or tungsten-halogen lamps were used for dimming, replace them with high-efficiency fluorescent lamps and dimmable electronic ballasts, which can achieve a wide range of dimming from 2% to 100%.
It should be noted that only well-designed electronic ballasts can take advantage of the above advantages. Although both are electronic ballasts, electronic ballasts for metal halide lamps are much more complicated than those for fluorescent lamps, or almost completely different. If the design or manufacturing process is not in place, a very small omission will cause failure.

Product Description
Electronic ballasts can be divided into 4 series and 15 varieties:
1. One-to-one, ordinary type and light box type special electronic ballasts are divided into 6 varieties of 20W, 30W, 40W
2. One for two, ordinary type and light box type special electronic ballasts are divided into 6 varieties of 2 X 20W, 2 X 30W, 2 X 40W
3. Electronic ballasts for ring lights are divided into 3 varieties: 22W, 32W and 40W
4. Quartz germicidal lamp ballast is suitable for 35-60W, a total of 1 variety
Note: 20W and 40W are for T10 and T12 tubes, and 18W and 36W are for T8 lamps. So sometimes when we talk about 20W, it can also be understood as 18W. At the same time, we can also understand the 36W of T8 tube as 40W of T10 and T12, because their ballasts are common.

Cautions
Electronic ballast with utility direct rectification, and then half-bridge inverter, lighting fluorescent tubes. It is not isolated from the mains, as the hot base plate of the TV, the circuit board is charged everywhere, human contact with the public line (ground) are at risk of electric shock, pay special attention to personal safety during maintenance. After adding electricity, do not touch any metal part of the circuit board with your hands, especially do not take the circuit board with both hands. Remove the lamp during maintenance, take out the two circuit boards A and B from the plastic cover of the two R ends of the lamp holder, solder the four wires 1-4 of the filament spring piece, solder them to the filament pins on both ends of the lamp in turn, and connect the switch SWi and power plug at the utility introduction end. Connected to 5w1 is very necessary. In the maintenance found that not connected to SW1, in the process of plugging and adding power, many times damage electronic ballast, this is because the plugging process, there are often multiple pass, break, which will produce a very high sharp pulse voltage breakdown vulnerable components.

Extended Reading
 FAQ
FAQ
-
Are electronic ballasts compatible with all types of gas discharge lamps?
While electronic ballasts can be used with various types of gas discharge lamps, such as fluorescent and high-intensity discharge (HID) lamps, it is essential to select the appropriate ballast for the specific lamp type and wattage. Using an incompatible electronic ballast may result in reduced lamp performance, premature lamp failure, or even damage to the ballast or lamp. Always consult the manufacturer's guidelines and specifications when selecting an electronic ballast for a particular lamp.
-
What are the advantages of electronic ballasts over magnetic ballasts?
Electronic ballasts offer several advantages over magnetic ballasts, including: Higher energy efficiency: Electronic ballasts consume less power and produce less heat, resulting in lower energy costs. Improved lamp performance: Electronic ballasts provide a more consistent and stable current to the lamp, ensuring optimal performance and reducing flickering. Lightweight and compact design: Electronic ballasts are generally smaller and lighter than their magnetic counterparts, making them easier to install and maintain. Dimming capabilities: Many electronic ballasts have built-in dimming features, allowing for greater control over the light output.
-
What is the primary function of an electronic ballast?
The primary function of an electronic ballast is to regulate the current flowing through a gas discharge lamp, such as a fluorescent or high-intensity discharge (HID) lamp. Electronic ballasts provide a stable and consistent supply of power, ensuring that the lamp operates efficiently and extends its lifespan.
Popular Blogs
-
What is Integrated C...
IC design, short for integrated circuit design, ...
-

Types and Applicatio...
As the world continues to search for sustainable...
-
What is an Analog In...
An analog integrated circuit mainly refers to an...
-

What Can ChatGPT Bri...
ChatGPT's popularity continues, and although it ...
Hot Products
-

-

-

Infineon Technologies Corporation
INFINEON - IFX9201SGAUMA1 - MOTOR CONTROLLER, HALF...
-
Infineon Technologies Corporation
solar inverters as well as SMPS and uninterruptibl...
-
Microchip Technology, Inc
32-bit Microcontrollers - MCU PIC32MK, 1MB Flash, ...
-

-

-

-
-

-

-
-

-
-

-
-
-

-

Infineon Technologies Corporation
EV charging: Off-board charging, where users can ...
-

-
-

-

-
-

-

-

-

-

-

-

-

-

-

-
-
-
-
-

-

-

-

-
-

-
-
-

-
-

-









