Define 2200(2.2k) Ohm Resistor, Color Code, Uses
Update Time: Jun 12, 2023 Readership: 4056
Contents
In the realm of electronics, resistors play a vital role in controlling and regulating the flow of electric current. Among the diverse range of resistors available, the 2200-ohm resistor, commonly represented as 2.2k, holds significance. This article aims to explore the definition of the 2200-ohm resistor, decipher its color code, and shed light on its various applications in electronic circuits. By unraveling the intricacies of this essential component, we can deepen our understanding of its functionality and unleash its potential in electrical engineering.
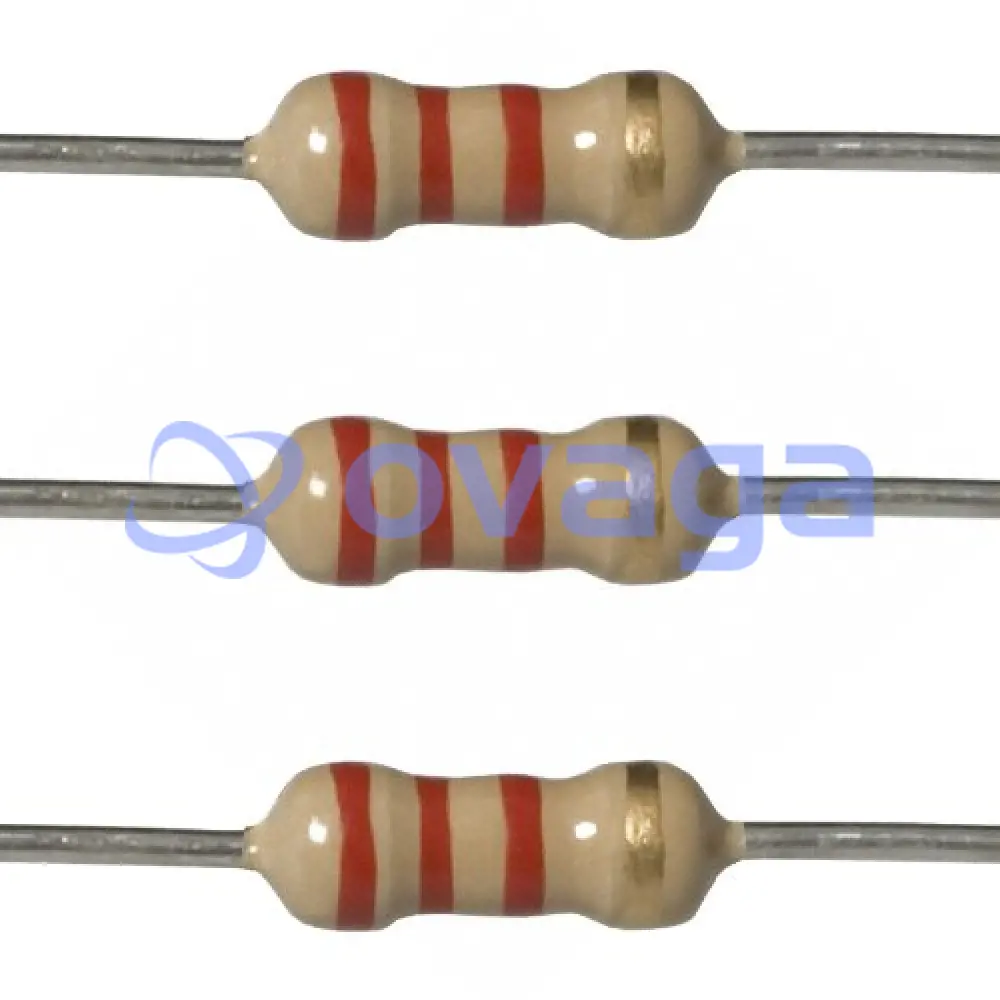
What is a 2200 Ohm Resistor?
A 2200-ohm resistor is an electrical component that is used to impede the flow of electric current in a circuit. It is designed to offer a resistance of 2200 ohms, which means that it restricts the amount of current that can pass through it. Resistors are passive components that dissipate electrical energy in the form of heat when current flows through them.
The 2200-ohm resistor is commonly represented using the numerical value of 2200 ohms or as 2.2k (kilo-ohms). It is a standard resistor value that is widely available in electronic component stores.
Resistors are essential in electronic circuits for various purposes. They can be used to limit current flow, divide voltages, and provide load resistance, among other applications. The 2200-ohm resistor is often used in circuit designs where a specific resistance value is required to achieve the desired electrical characteristics or to protect components from excessive current.
By incorporating a 2200-ohm resistor into a circuit, engineers and designers can precisely control the behavior of the circuit, ensuring safe and efficient operation.
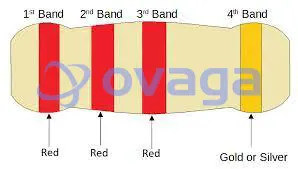
2.2k Ohm Resistor Color Code
The color code for a 2.2k-ohm resistor typically consists of four color bands. Each color represents a specific numerical value or multiplier. The standard color code for a 2.2k-ohm resistor is:
Red - Red - Red - Gold
Breaking down the color code:
- The first red band represents the digit 2.
- The second red band represents the digit 2 as well.
- The third red band signifies the multiplier 10^2, which equals 100.
- The gold band indicates the tolerance level, which specifies the acceptable range of the resistor's actual resistance value.
Therefore, a 2.2k-ohm resistor with this color code would have a resistance value of 2200 ohms or 2.2 kilo-ohms, with a tolerance of 5% (gold band).
Features
Here's the information about the 2.2k ohm resistor presented in a table format:
| Feature | Description |
| Resistance Value | 2.2 kilo-ohms (2200 ohms) |
| Power Rating | Typically 0.25 watts to 0.5 watts |
| Tolerance | ±5% |
| Temperature Coefficient |
Typically around 100 parts per million per degree Celsius (100 ppm/°C)
|
| Operating Temperature | Typically -55°C to +155°C |
| Maximum Voltage Rating |
Varies depending on the resistor's construction and power rating
|
| Material |
Carbon film, metal film, or other resistor materials
|
| Package Type |
Commonly available in axial lead (through-hole) and surface mount packages
|
| Size |
Varies based on the power rating and package type, ranging from small to large
|
| Construction |
Typically composed of a resistive element, leads, and protective coating
|
| Stability |
Offers stable resistance over a wide temperature range
|
These features collectively contribute to the functionality and reliability of the 2.2k ohm resistor, making it suitable for a wide range of applications in electronic circuits, such as voltage dividers, current-limiting circuits, signal conditioning, and many other circuit designs that require precise resistance values.
Uses
The 2.2k ohm resistor, with its specific resistance value, finds application in various electronic circuits. Some common uses of the 2.2k ohm resistor include:
1. Voltage Dividers: In voltage divider circuits, the 2.2k ohm resistor is often used in conjunction with other resistors to create a specific output voltage. By strategically placing the 2.2k ohm resistor in the divider network, it helps in dividing the input voltage and generating the desired output voltage.
2. Current Limiting: The 2.2k ohm resistor is frequently employed as a current-limiting resistor. By connecting it in series with an LED or other components, it restricts the flow of current to a safe and desired level, preventing damage to the components.
3. Pull-up and Pull-down Resistors: In digital circuits, the 2.2k ohm resistor acts as a pull-up or pull-down resistor. It ensures that inputs to digital devices have a stable voltage level when they are not actively driven by other components, thereby preventing floating inputs.
4. Signal Conditioning: The 2.2k ohm resistor is used in signal conditioning circuits to modify or adapt signals to suit the requirements of subsequent circuitry. It can be part of filter networks, attenuators, or voltage dividers to condition signals for optimal processing.
5. Amplifier Biasing: In amplifier circuits, the 2.2k ohm resistor is employed in biasing networks. It helps establish the required bias voltage levels for proper transistor or operational amplifier operation, ensuring stable and accurate amplification.
6. Oscillator Circuits: The 2.2k ohm resistor can be utilized in oscillator circuits to set the frequency or timing characteristics of the oscillation. It is often part of the feedback network, determining the timing intervals and waveform generation.
7. Analog-to-Digital Conversion: The 2.2k ohm resistor can be used in voltage divider networks as part of analog-to-digital conversion circuits. It helps in scaling down the input voltage range to match the operating range of an analog-to-digital converter (ADC).
How to Make a 2.2k Ohm Resistor?
Creating a precise 2.2k ohm resistor from scratch is a complex and specialized process that often requires advanced manufacturing techniques and equipment. It involves careful control of resistor material, size, and other factors to achieve the desired resistance value. So making your own 2.2k ohm resistor is not practical for most people.
Resistors are manufactured using specific materials and processes to ensure their reliability, stability and accuracy. Resistive elements are typically made of carbon films, metal films, or other resistive materials that are precisely deposited or etched onto a substrate. Precisely control the size and composition of the resistive element to achieve the desired resistance value.
To produce resistors with consistent resistance values such as 2.2k ohms requires a highly controlled manufacturing process in specialized facilities. These processes involve precision equipment and techniques such as thin film deposition, laser trimming and quality control testing to ensure resistors meet specified resistance tolerances and performance standards.
For most practical purposes, it is more feasible and reliable to obtain commercially manufactured 2.2k ohm resistors from electronic component suppliers. These resistors are readily available, affordable, and manufactured under controlled conditions that ensure their accuracy and performance.
Average Price
The average price of a 2.2k ohm resistor can vary based on factors such as brand, quantity, package type, and quality. Generally, the average price is around $0.05 to $0.15 per unit.
It is important to note that prices fluctuate over time due to factors such as supply and demand, market conditions, and specific suppliers. Also, buying in bulk or from a wholesaler may offer a discounted price compared to buying individual resistors.
For the most accurate and up-to-date pricing information, it is recommended to consult an electronic component supplier or an online retailer that specializes in resistors. They will provide you with specific pricing based on your requirements and current market conditions.

2.2k Ohm ¼ Watt Resistor
A 2.2k ohm 1/4-watt resistor refers to a resistor with a resistance value of 2.2 kilo-ohms (2200 ohms) and a power rating of 1/4 watt. The power rating specifies the maximum power the resistor can dissipate without overheating or getting damaged.
A 1/4-watt power rating is a common specification for resistors used in low-power electronic circuits. It indicates that the resistor can safely handle up to 0.25 watts of power without experiencing significant temperature rise. It is important to ensure that the power dissipated in the resistor remains within this specified limit to avoid thermal damage or deviation from the resistor's performance characteristics.
The 2.2k ohm 1/4-watt resistor is widely available and commonly used in various electronic applications, including voltage dividers, signal conditioning circuits, current limiting, biasing networks, and many other circuit designs. It is generally considered a standard power rating for general-purpose resistors and can be found in different package types, such as axial lead (through-hole) or surface mount resistors.
2.2k Ohm 1 Watt Resistor
A 2.2k ohm 1-watt resistor refers to a resistor with a resistance value of 2.2 kilo-ohms (2200 ohms) and a power rating of 1 watt. The power rating indicates the maximum power that the resistor can safely dissipate without overheating or getting damaged.
A 1-watt power rating signifies that this resistor can handle up to 1 watt of power without experiencing significant temperature rise. This higher power rating makes it suitable for applications where higher power levels are involved, such as in power supply circuits, amplifiers, or circuits that require significant current flow.
The 2.2k ohm 1-watt resistor is designed to withstand higher power dissipation and is typically larger in size compared to resistors with lower power ratings. It ensures better heat dissipation and can handle greater electrical stress without compromising its performance or integrity.
It is important to select a resistor with a power rating that matches or exceeds the power requirements of the circuit to ensure reliable operation. Using a resistor with a power rating lower than what the circuit demands may result in overheating, potential failure, or alteration of its resistance value.
The 2.2k ohm 1-watt resistor is commonly available in different package types, including through-hole (axial lead) resistors, which facilitate easy mounting and soldering into circuit boards or other electronic assemblies.
Conclusion
All in all, a 2.2k ohm resistor has a defined resistance value and power rating and is an important component in electronic circuits. Its ability to control and regulate electrical currents has applications in various fields of electronics and electrical engineering. By exploring the intricacies of the 2.2k ohm resistor, deciphering its color code, understanding its properties, and recognizing its diverse uses, we gain a deeper understanding of its significance in circuit design. Whether used in voltage dividers, current limiting circuits, or signal conditioning applications, the 2.2k ohm resistors provide the necessary control and stability for optimal circuit performance.
Extended Reading
 FAQ
FAQ
-
Are there any specialized variants of the 2200-ohm resistor available?
Yes, there are specialized variants of the 2200-ohm resistor available to meet specific application requirements. For example, precision resistors with tighter tolerance values (e.g., 1% or 0.1%) may be used in applications where precise resistance values are crucial. Additionally, temperature-compensated resistors or high-temperature resistors may be used in environments with extreme temperature conditions to maintain stable resistance values.
-
What are the voltage limitations of a 2200-ohm resistor?
The voltage limitations of a 2200-ohm resistor depend on factors such as its power rating and construction. Typically, a 1/4-watt 2200-ohm resistor can handle voltages within the range of a few volts to tens of volts, while a 1-watt 2200-ohm resistor can withstand higher voltages, potentially up to a few hundred volts. It is important to consider the power rating and voltage requirements of your specific application when selecting a resistor.
-
Can I use multiple 2200-ohm resistors in series or parallel to achieve a different resistance value?
Yes, you can combine multiple 2200-ohm resistors in series to increase the total resistance or in parallel to decrease the total resistance. For example, two 2200-ohm resistors in series would yield a total resistance of 4400 ohms, while two 2200-ohm resistors in parallel would result in a total resistance of 1100 ohms.
Popular Blogs
-

NTC 103 Thermistor: ...
Thermistor 103 is a type of NTC thermistor, with...
-
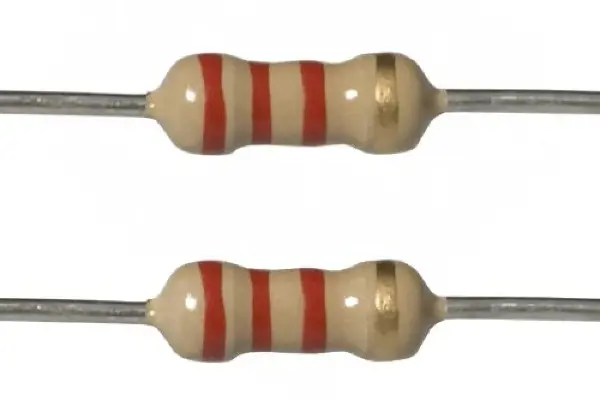

Define 2200(2.2k) Oh...
A 2200-ohm resistor is an electrical component t...
-

What is a 10k Resist...
The 10k resistor is a type of resistor, and we u...
-

Safeguarding Electri...
A neutral earthing resistor (NGR) is an electric...














